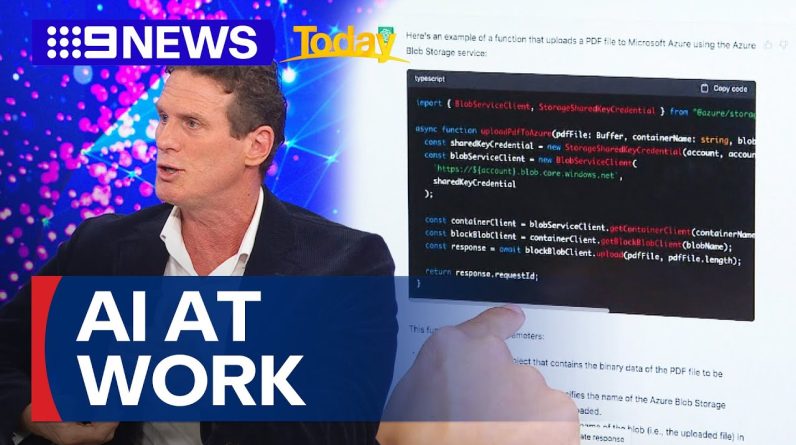
Google is launching an Artificial Intelligence powered chatbot called Bard to rival ChatGPT. Bard will be used by a group of testers before being rolled out to the public in the coming weeks, the firm said. ChatGPT can answer questions and carry out requests in text form, based on information from the internet as it was in 2021. But the ultimate aim of chatbots lies in internet search, experts believe – replacing pages of web links with one definitive answer.

What is Google Bard?
Google Bard is an experimental conversational AI service that will be released to the public in “the coming weeks”. Like its ChatGPT rival, Bard will use state-of-the-art language models and technologies.
The chatbot is built on a ‘large language model’ (LamDA) that has been trained on vast troves of data and can generate text with incredible skill. It also has a range of other talents including image generation, music creation and translation.
What is Bard?
Google Bard is a conversational AI chatbot that can answer questions about a variety of topics. It draws on information from the web to offer fresh, high-quality responses.
Unlike its rival, ChatGPT (which is also backed by Microsoft) that relies on the GPT-3 language model, Bard is based on Google’s own language model called LaMDA, which was created by a former Google engineer and has been described as “sentient.” It can generate text with incredible skill.
In a demo of Bard, a user asked it to explain new discoveries made by Nasa’s James Webb Space Telescope to a nine-year-old. It then spit out three answers, each of which included a link to relevant information on the web.
The new chatbot is available to a small group of “trusted testers” ahead of a wider rollout in early 2023, Google’s Sundar Pichai wrote in a blog post on Monday. It uses a version of LaMDA that requires less computing power to serve more users and improve with feedback, Pichai said.
As of this writing, Bard is only available to a select group of testers who are expected to give it a lot of feedback and help make it better. It will also undergo internal and external testing to ensure it meets a high bar for quality, safety and groundedness in real-world information, according to Pichai.
At present, it is unclear how many questions Bard can answer, or how much knowledge it possesses. In a demo of the chatbot, it was able to answer a query about two Oscar-nominated movies and planned a friend’s baby shower.
In addition to its ability to answer queries about a wide range of topics, Bard is capable of synthesizing complex information into bite-sized pieces that are easier for humans to understand. For example, it can tell you about the best strikers in football right now and how to train to emulate them.
Bard will be a major competitor to ChatGPT, which was created by OpenAI and is backed by Microsoft. However, Google says it will differentiate itself from the competition by “drawing on the breadth of the world’s knowledge with the power, intelligence and creativity of our AI.”
How does Bard work?
Google Bard is an artificial intelligence-powered chatbot that can answer questions and give answers to other users. It competes with the fast-emerging ChatGPT, which is backed by Microsoft and has attracted tens of millions of users since it launched late last year.
According to Google, Bard uses online information to give fresh, high-quality replies to users’ questions. It can also condense and extrapolate information to create new information.
The AI engine behind Google Bard is called LaMDA, which stands for Language Model for Dialogue Applications. It was announced two years ago at the 2021 Google I/O keynote as a next-generation language and conversation engine.
It has the ability to learn from users’ feedback, and combines that with Google’s own internal testing to ensure Bard is “safe” and grounded in real-world information.
As such, it could be used to teach a nine-year-old about recent scientific discoveries made by NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, for example. The company says it can also be used to find the latest sports scores and automate tasks like making restaurant reservations or booking flights.
In the coming weeks, Bard will be available to “trusted testers” ahead of general release. It will be integrated into Google Search, YouTube and other products.
While it’s not yet publicly available, Google said its selected testers will be able to use the chatbot icon on their device to type queries and get answers back from Bard. The company will then use that feedback to improve its product further.
Currently, Bard is only available for a limited number of people and uses a “lightweight” version of LaMDA that requires significantly less computing power. The goal is to make it faster and more accessible for testing purposes.
The new model also allows Bard to respond more quickly to user queries. Its responses are likely to be more accurate than those of ChatGPT, as it will draw on a wider range of information from the internet.
But, just like any AI, Bard will still need to be constantly updated with new information. This means that it will need to be able to cope with changes in the news and social media.
What are the benefits of Bard?
Google Bard is a new AI-powered chatbot that is now available to a limited number of select testers. This product is being launched as part of the company’s AI-powered search initiative, which seeks to improve its ability to understand user queries and deliver relevant results.
This new bot is built upon Google’s language model for dialogue applications (LaMDA), a major AI engine that Google unveiled in 2021. It helps users quickly and easily find the answers they need by using advanced machine learning algorithms to understand the intent behind their queries.
With Bard, you can ask it questions in a natural language format, just like you would when talking to a friend. Then, the bot will process your query and respond with a response that it understands.
To answer a question, the AI-powered chatbot will use its largest knowledge base to generate a response that is both informative and natural-sounding. This makes it a great tool for students in school to explain complex subjects in simple terms.
The bot can also be used as a social hub, helping you interact with friends in a conversational manner. For example, if you’re in a group and want to know whether a certain restaurant is open or if a movie theater is showing the movie you are interested in, the chatbot can automatically search for these types of information through its vast database.
It can also be used as a personal assistant, helping you to automate tasks that require human interaction. For example, the AI-powered chatbot will help you to book a restaurant reservation or a flight for you and your family.
Bard is based on a smaller version of LaMDA, which is a highly advanced AI model, as well as Transformer technology that was pioneered by Google in 2017. This lightweight version of the AI engine requires “significantly less computing power” to scale to more people and gather feedback more quickly, the company said.
With Bard, Google seeks to bring a new level of intelligence and creativity to the web. It combines the breadth of world’s knowledge with the power, intelligence and creativity of its large language models to provide fresh, high-quality responses that are unique and original.
What are the limitations of Bard?
Google Bard is an experimental conversational AI service developed by the search giant that aims to provide users with quick and accurate answers. The AI is based on a large language model called LaMDA, which uses deep learning algorithms to generate human-like text responses.
The chatbot is a new addition to Google’s search engine and is designed to give users answers instead of just a list of web pages. However, it is still a work in progress and will be released only to a select group of trusted testers.
Bard is an AI that provides users with answers to questions that have been inputted in the search bar. Unlike other search engines, it focuses on providing quick and accurate answers, rather than just providing a list of websites.
While the technology is impressive, there are some limitations to using Bard. One of the most important limitations is that it can’t produce prose in the vein of William Shakespeare.
Despite these limitations, Bard can be useful for finding information and answering questions online. But it is also important to use critical thinking skills and always fact-check the information you receive from Bard.
As an AI, Bard is prone to fabricating information and may also be biased toward certain groups of people. It is therefore not suitable for all applications.
Although the Bard AI chatbot is an experimental service, it has the potential to revolutionize the way we search for information online. It is also an excellent tool for teachers to help their students find the right information and answer questions.
It is also a good tool for businesses who want to implement AI-powered search. Business owners can use it to analyze data and make decisions quickly.
In addition, it can be used to generate content such as advertisements and articles. These types of articles can help businesses gain a competitive edge in the market.
Google has made it a priority to invest in artificial intelligence and bring AI-powered features to its search platform. Bard is the company’s latest effort to adapt its AI research and development to real-world problems.
AI Writers: The Future of Journalism?
The field of journalism is changing drastically, as it has been since the invention of the printing press. With the rise of digital media, new technologies have begun to shape the way journalists create and distribute content. One such technology is Artificial Intelligence (AI) writing, where an AI program can automatically generate written content on a wide range of topics. This raises the question: Could AI writers be the future of journalism?
Let’s start by looking at what AI writers are capable of. Thanks to advances in artificial intelligence and natural language processing algorithms, AI writers can generate articles quickly and accurately on a variety of topics. In some cases, these articles may even pass for human-written pieces, depending on their level of sophistication. Even now, there are several news organizations using automated systems to create stories about sports, finance and other minor topics using publicly available data sources such as statistical feeds or company reports.
But could AI eventually take over more complex tasks like investigative reporting or opinion writing? While this may seem far-fetched at first glance, there is evidence that suggests this could become a reality soon. For example, GPT-3 (Generative Pre-trained Transformer 3), an advanced natural language processing algorithm developed by OpenAI in 2020, was able to generate convincing essays with minimal input from users and no prior training data specific to any given task. Moreover, recent advances in deep learning have enabled bots to fetch primary resources such as court records or interview archives and then compose them into coherent narratives – essentially doing the work that would normally require hours or days of research.
Given these capabilities, it’s easy to see why many people are optimistic about what AI-generated content could bring to journalism. It could mean faster turnaround times for news delivery without sacrificing quality; it could enable deeper analysis thanks to its ability to process large amounts of data; and it could help unearth hidden trends due to its machine learning capabilities. However, it might also lead to greater levels of disinformation if not used responsibly; there’s always a risk when relying solely on algorithms for generating content without editorial oversight from humans. Nonetheless, despite these potential issues it’s clear that artificial intelligence holds great promise for journalism in terms of speed and efficiency gains – allowing reporters more time for meaningful investigation rather than mundane fact checking or data gathering tasks.
So while we may not quite be ready for robot reporters just yet (we’ll leave that up to sci-fi movies!), AI writing already shows great potential as an effective supplement (or even replacement) for human Journalists in certain cases – particularly those involving repetitive tasks or large amounts of data processing which machines excel at handling with consistent accuracy across different types/topics/subjects etc… We should be excited by what this technology might bring us moving forward – but also mindful that technology alone cannot replace the journalistic discretion humans possess when it comes filtering fact from fiction when composing stories about delicate subject matters like politics or international affairs!
AI Writing Tools to Help You Create Engaging Content
In today’s digital world, Artificial Intelligence (AI) powered writing tools are becoming increasingly popular. These AI-driven tools enable you to quickly and easily generate engaging content, including blog posts, tweets, social media posts and more. Here’s a list of some of the top AI writing tools currently available:
- GPT-3 – Developed by OpenAI in 2020, GPT-3 is an advanced natural language processing algorithm that can generate convincing essays with minimal input from users.
- ChatGPT and ChatGPT Plus – In its own words, ChatGPT is “an AI-powered chatbot developed by OpenAI, based on the GPT (Generative Pretrained Transformer) language model. It uses deep learning techniques to generate human-like responses to text inputs in a conversational manner.” ChatGPT Plus is the paid version of ChatPT
- Article Forge– Article Forge is an AI Content Generator tool that utilises Artificial Intelligence to scan millions of web pages on a given topic, analyzes the content, and rewrites it in its own language. Article Forge has a free trial.
- Jasper – An AI writing assistant that is creative, ethical and friendly, Jasper can write engaging content like social media posts, tweets, blog posts and short stories.
- GOCharlie – The first and only AI engine specifically designed for marketing, blog writing, article and eassay writing, is called GoCharlie. Charlie, your new AI marketer, and is great in creating the best social media marketing material. In order to achieve this, Charlie transforms images into flawless ad copy, creates posts and advertisements utilising tone and keywords, evaluates content for the best possible structure or audience appeal, and offers unique responses to reviews and comments. With GoCharlie users can join up for a free trial.
- Writebot – This AI-powered text editor provides personalized feedback on your writing in real time. It offers useful features such as style suggestions and grammar fixes to help improve your written work.
- Quillbot – Quillbot is a powerful text editor designed for professional content creation with its easy-to-use AI editing capabilities. It helps you correct spelling errors and typos as well as suggest synonyms for words or phrases that don’t quite fit your intended meaning.
- Copywritely – Copywritely is an automated copywriting tool that helps you identify weak areas in your content such as misused words or phrases, redundant sentences and more. It also provides tips on how to refine your text for better readability.
- Grammarly – Grammarly is a trusted grammar checking application which can be used to quickly detect common errors in your written work such as misspellings and punctuation mistakes.
Albion News is a great place to find informative, up-to-date news articles. We provide a wide range of unique articles that offer an interesting perspective on current events from around the world and from various different sources. You can easily search for the topics that matter most to you and explore in-depth pieces that provide insight into the issues and important debates occurring today. Albion News helps you stay informed with carefully researched and credible stories!